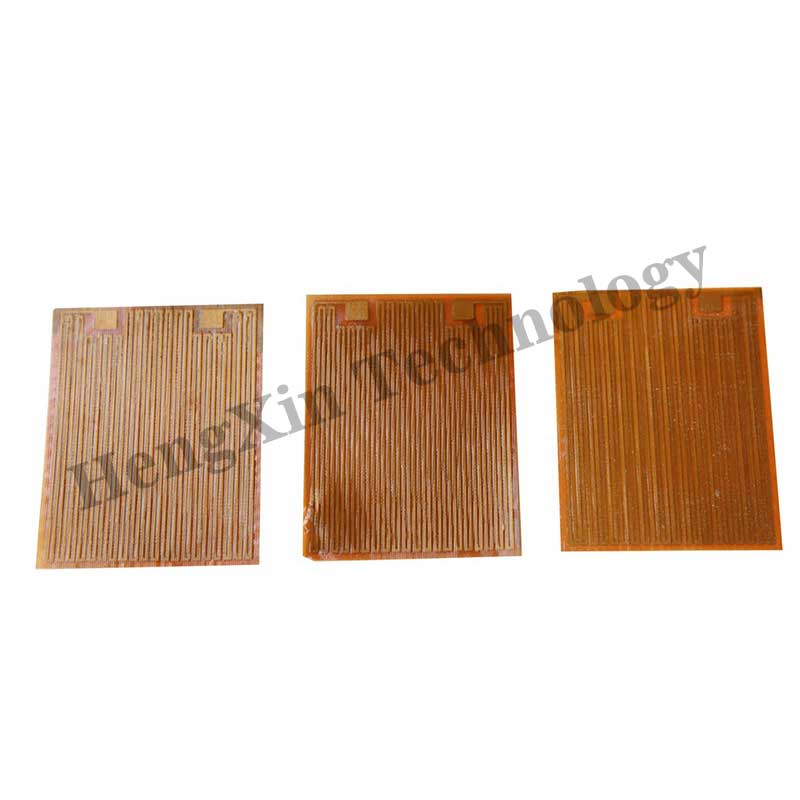
Teflon Film Heater and Pi Film Heater are both types of flexible, thin heating elements used in various applications where space constraints, precise temperature control, and uniform heating are essential. Here’s a detailed look at each type:
Teflon Film Heaters
Teflon film heaters are heating elements encapsulated in a Teflon (PTFE) film, known for its high chemical resistance, non-stick properties, and ability to withstand high temperatures.
Characteristics:
- Chemical Resistance: Teflon is highly resistant to a wide range of chemicals, making these heaters suitable for use in harsh environments.
- Temperature Range: Teflon heaters can typically operate in a wide temperature range, from -40°C to 300°C
- Non-stick Surface: The non-stick properties of Teflon prevent substances from adhering to the heater, making it easy to clean and maintain.
- Electrical Insulation: Teflon provides excellent electrical insulation, which enhances safety and reliability.
- Durability: Teflon film is tough and durable, resistant to wear and tear.
Applications:
- Chemical Processing: Used in environments where chemical resistance is crucial.
- Medical Devices: Suitable for sterilization processes and devices that require frequent cleaning.
- Aerospace and Military: Used in equipment exposed to harsh conditions.
- Food Industry: Utilized in applications where non-stick properties and cleanliness are vital.
PI (Polyimide) Film Heaters
PI film heaters are made with polyimide film, a high-performance plastic known for its excellent thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength.
Characteristics:
- Thermal Stability: PI film heaters can operate in a temperature range from -40°C to180°C
- Thin and Flexible: Polyimide film heaters are extremely thin (often less than 0.2 mm), making them ideal for applications with tight space constraints.
- Uniform Heating: They provide very uniform heating across the surface, essential for applications requiring precise temperature control.
- Chemical Resistance: Polyimide is resistant to many chemicals, making these heaters suitable for various industrial applications.
- Mechanical Strength: Despite being thin, PI film heaters have high tensile strength and durability.
Applications:
- Electronics: Used in heating elements for printed circuit boards (PCBs), LCD displays, and other electronic components.
- Medical Devices: Suitable for medical equipment requiring precise and uniform heating.
- Aerospace and Defense: Used in de-icing systems and other applications where reliability under extreme conditions is necessary.
- Laboratory Equipment: Ideal for analytical instruments and other laboratory devices requiring accurate temperature control.
Comparison and Selection
When choosing between Teflon film heaters and PI film heaters, consider the following factors:
- Chemical Resistance: Teflon heaters are more resistant to a broader range of chemicals compared to polyimide heaters.
- Temperature Range: Both types offer high-temperature resistance, but Teflon can handle slightly higher temperatures in some cases.
- Flexibility and Thickness: PI heaters are typically thinner and more flexible, making them better suited for applications with limited space.
- Mechanical Properties: PI heaters offer excellent mechanical strength even in thin formats.
- Application Requirements: Consider the specific needs of your application, including chemical exposure, temperature range, space constraints, and the need for uniform heating.
Both Teflon and PI film heaters are excellent choices for specific applications, and selecting the right one depends on the particular requirements of your project.